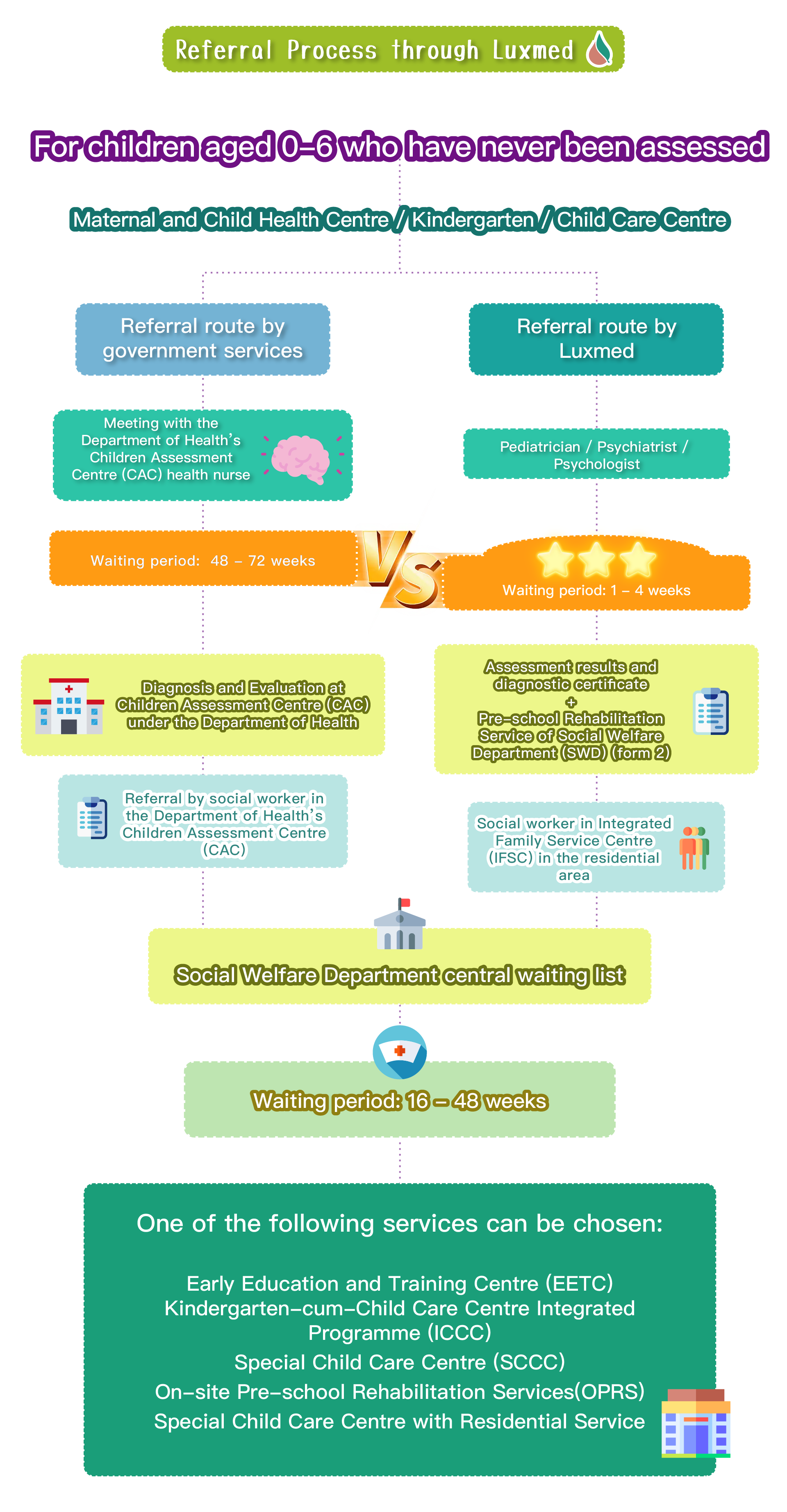
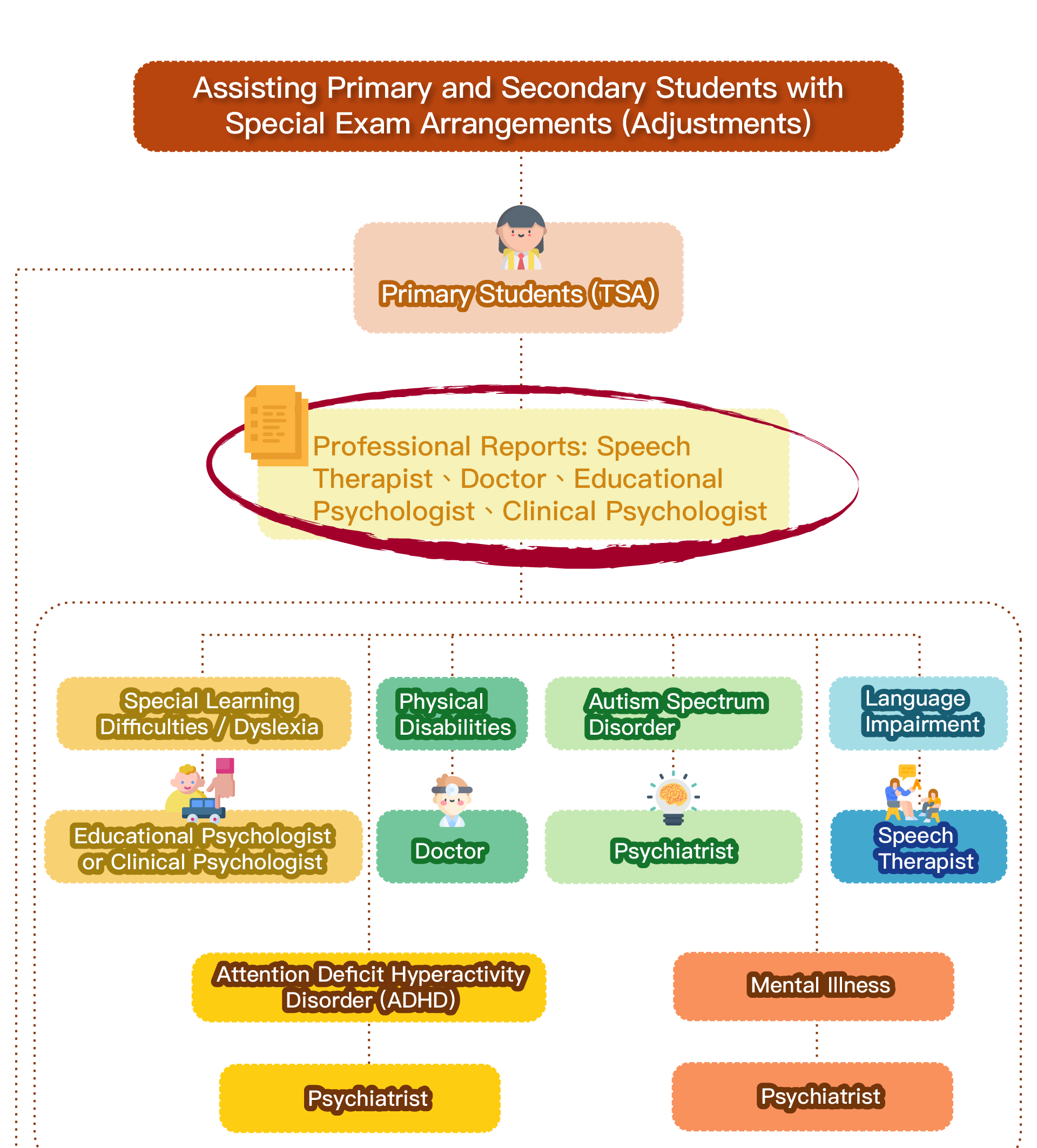
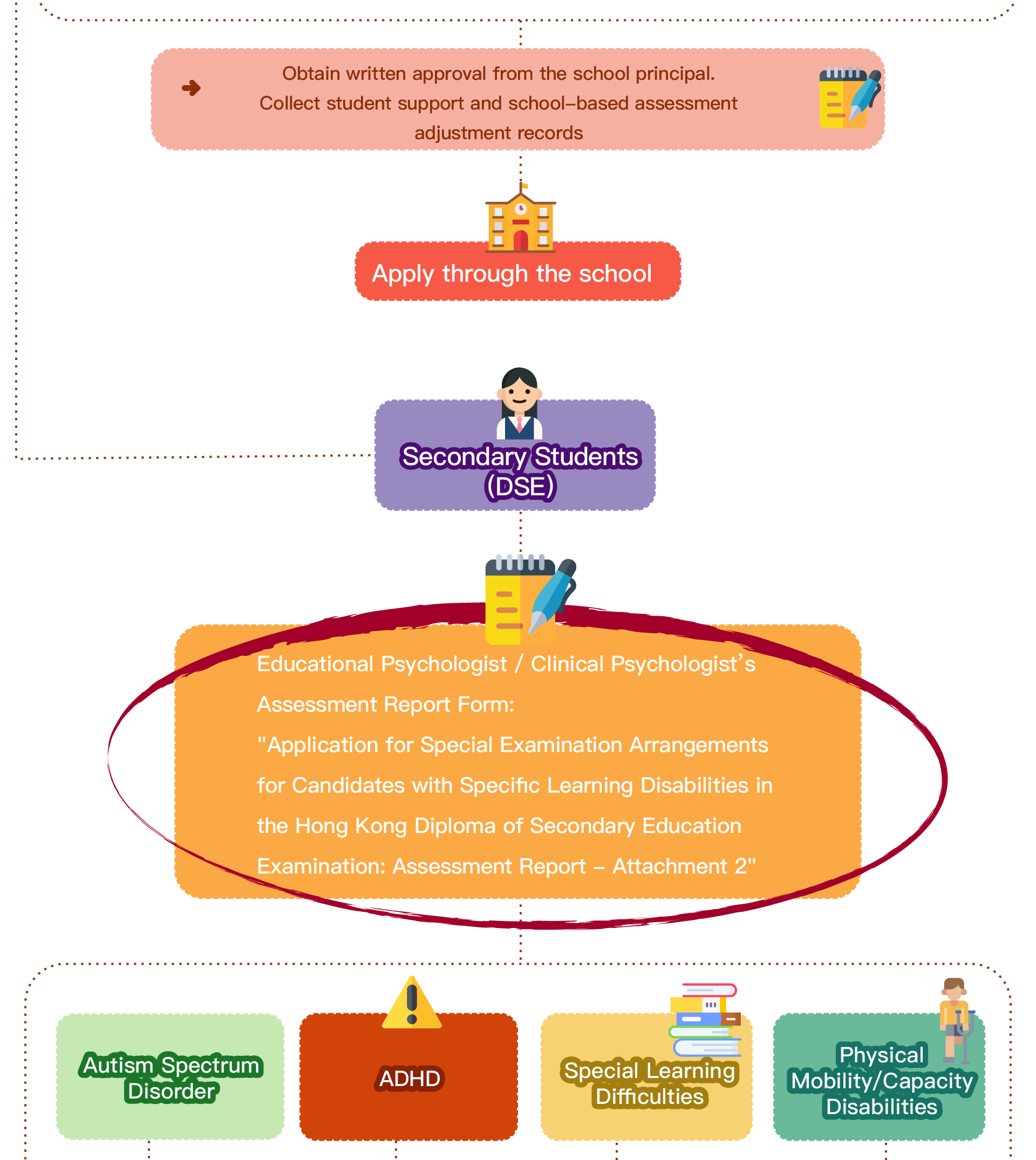
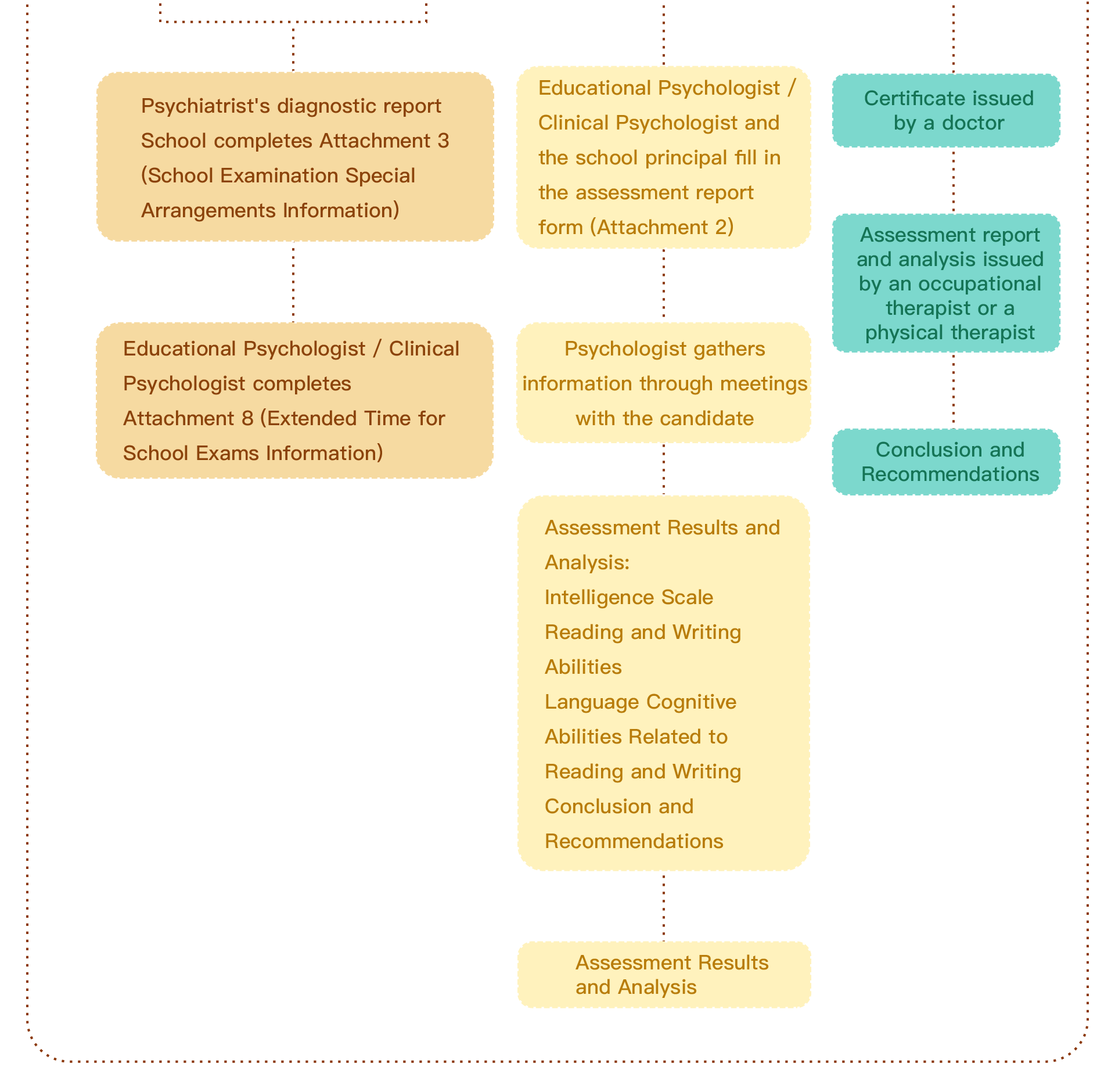
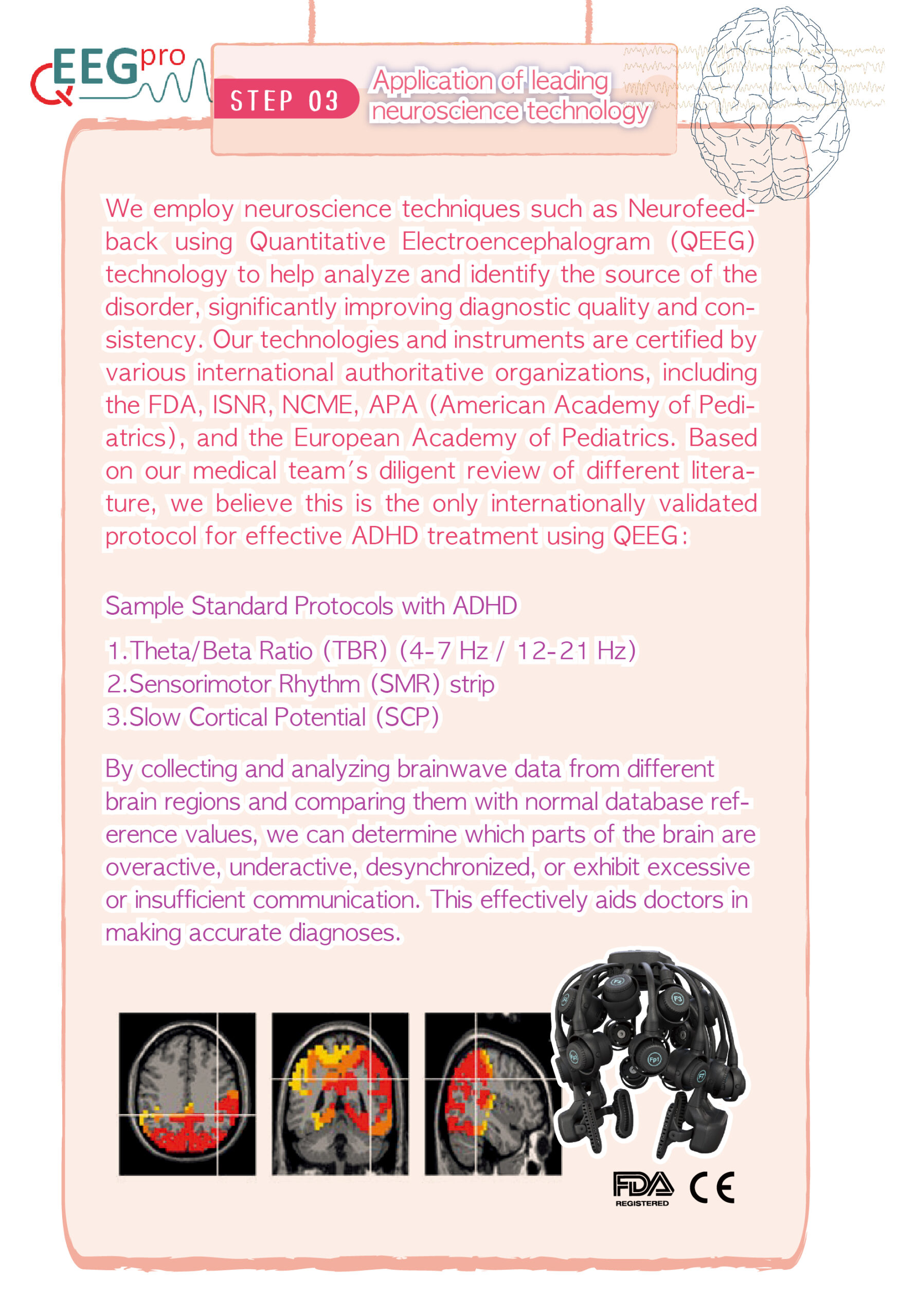
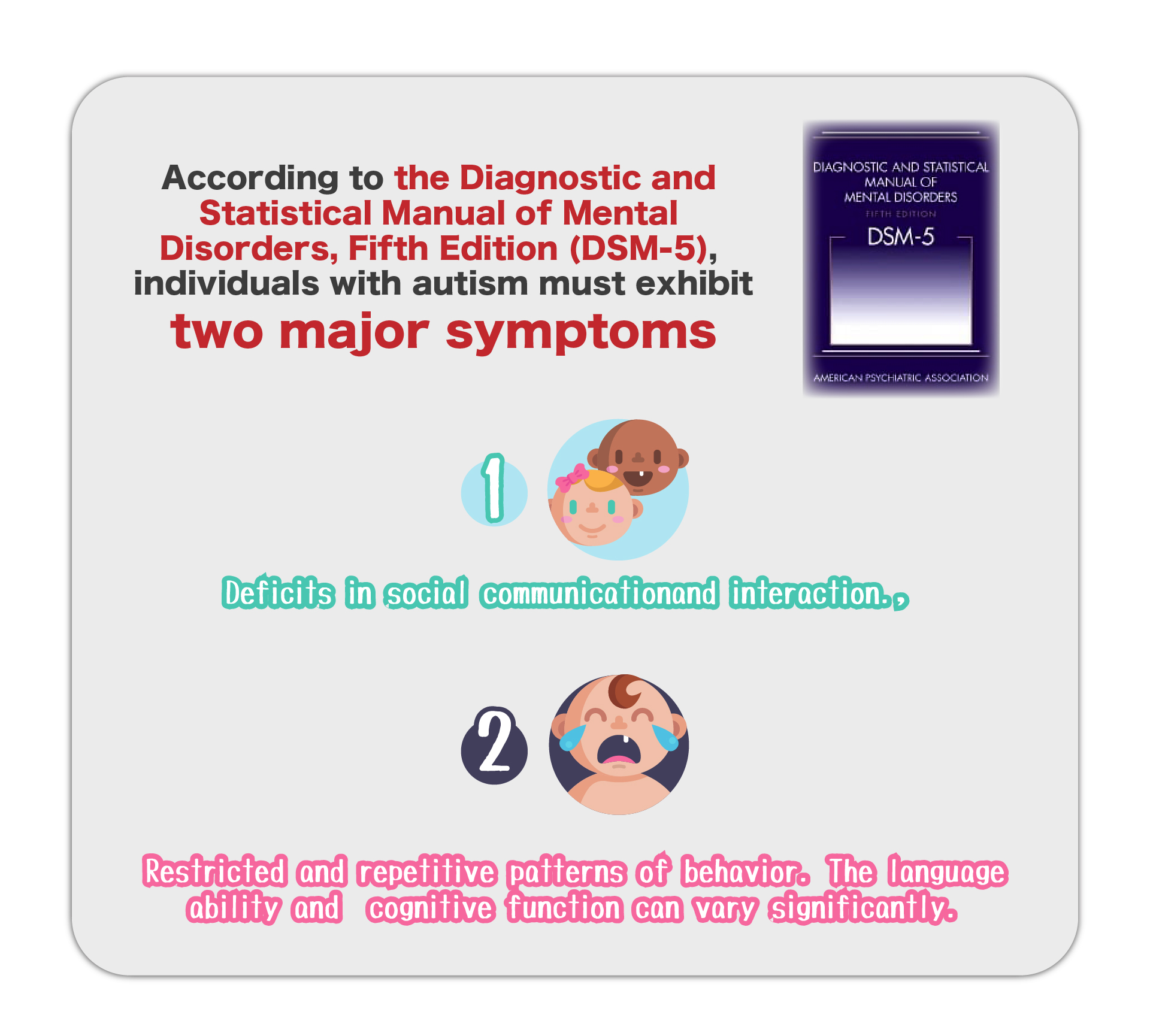
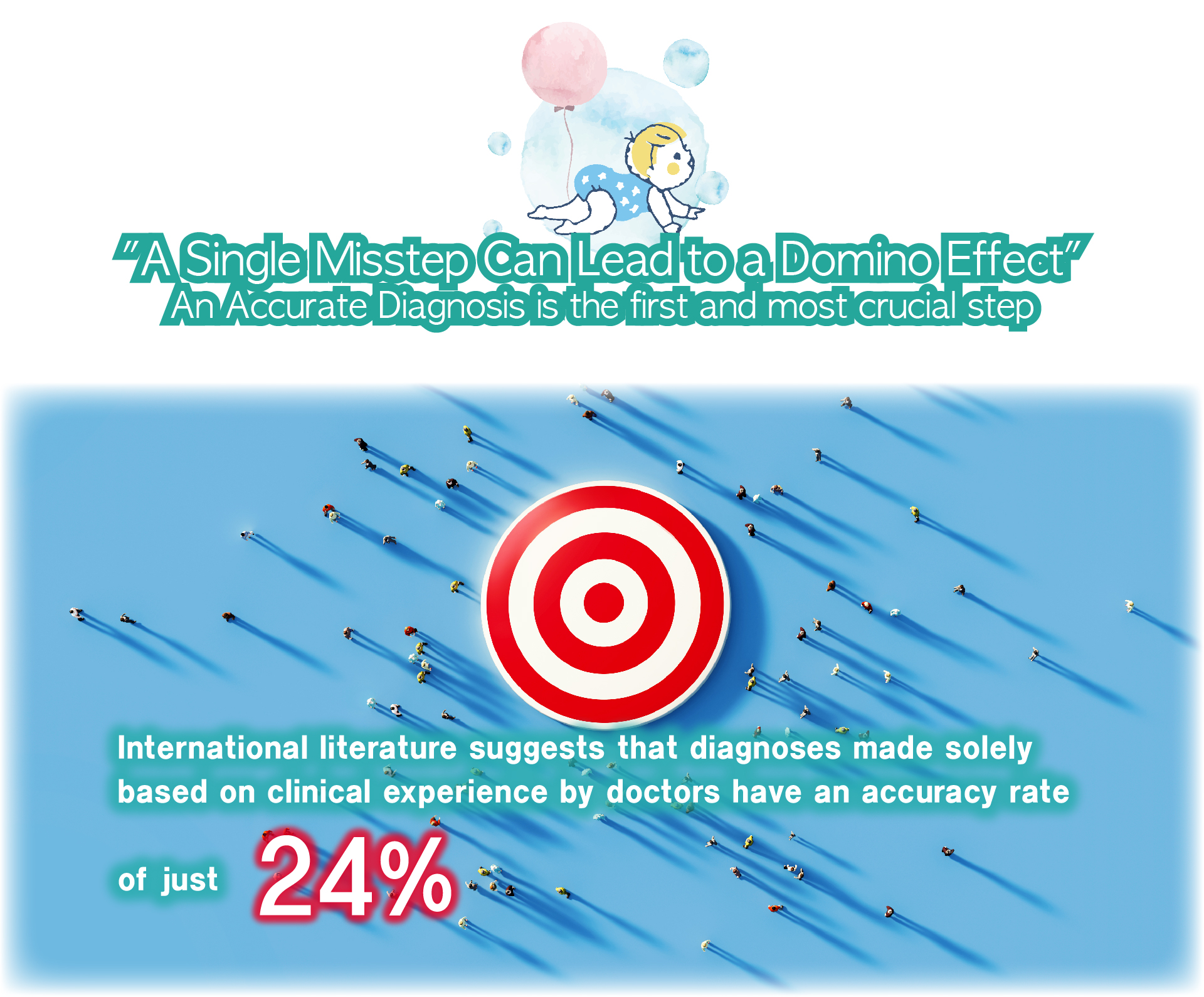
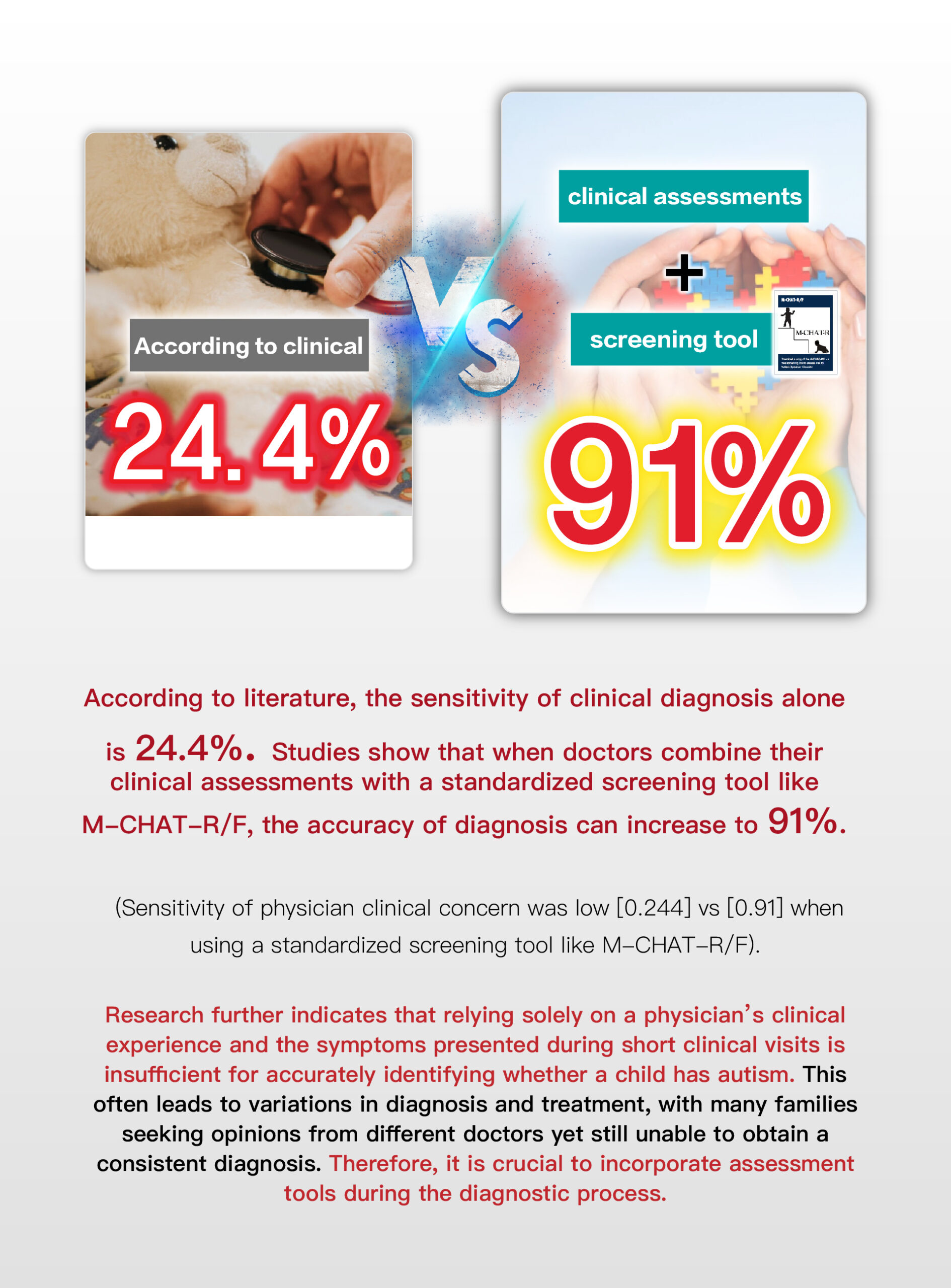
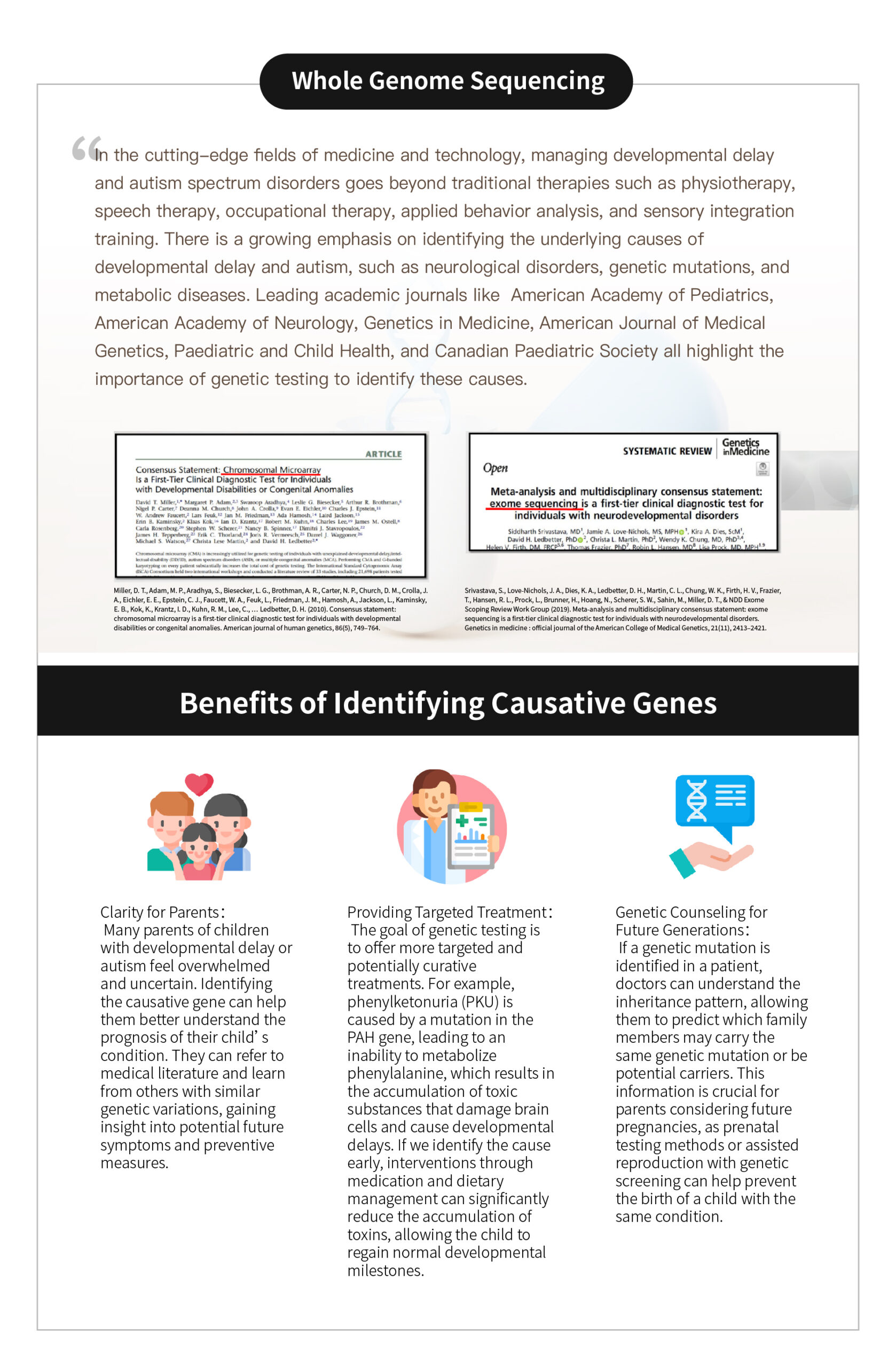
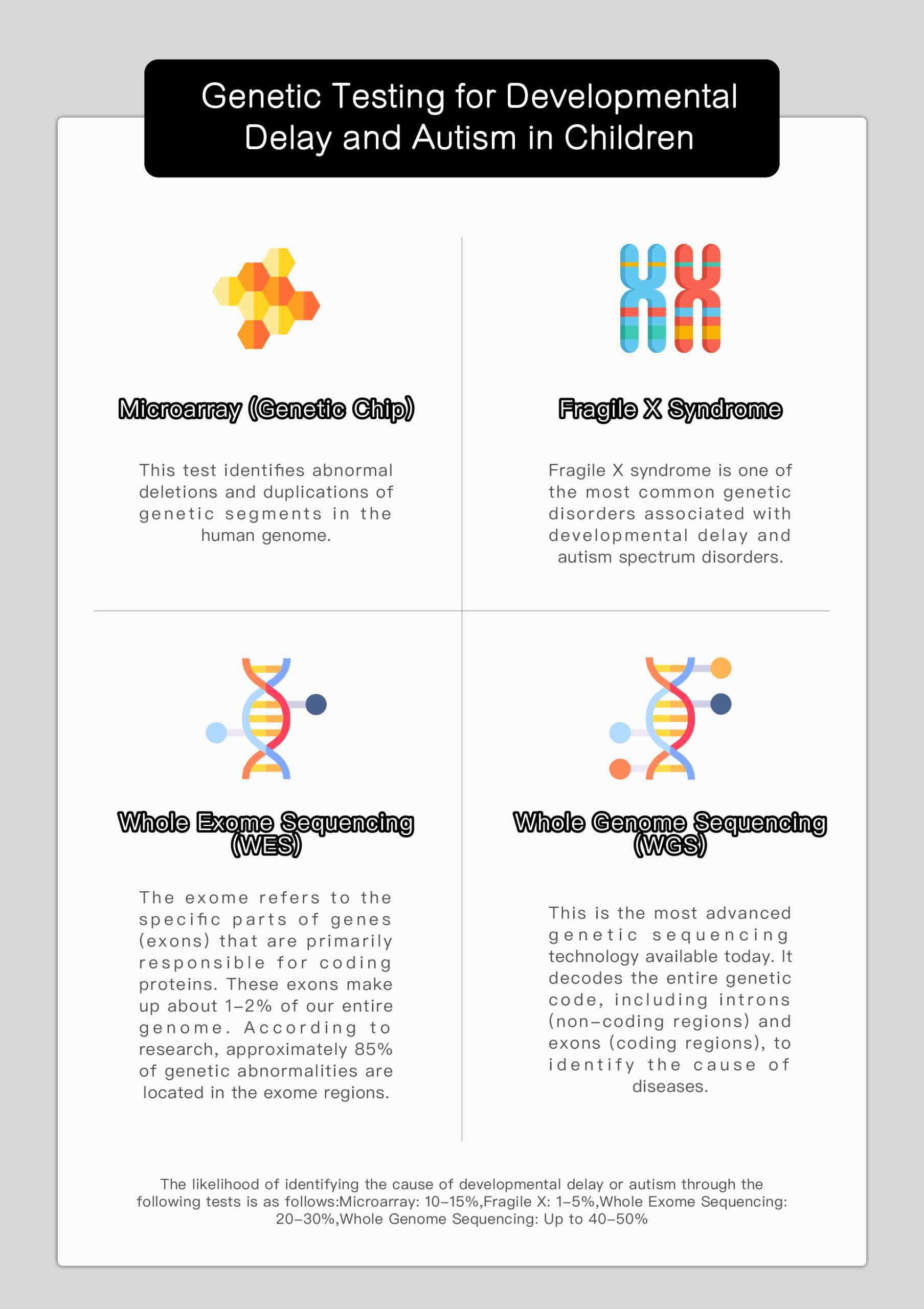
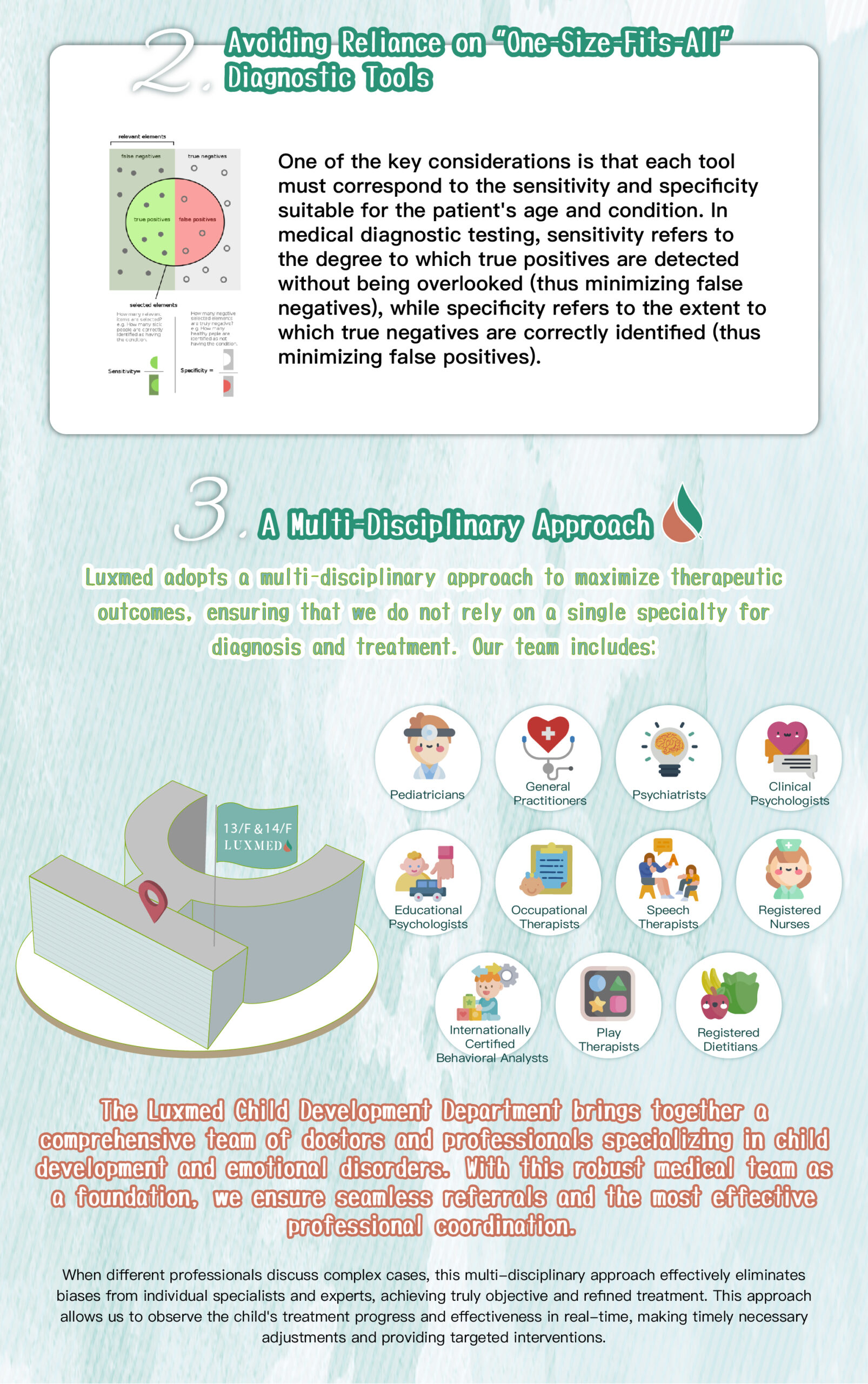
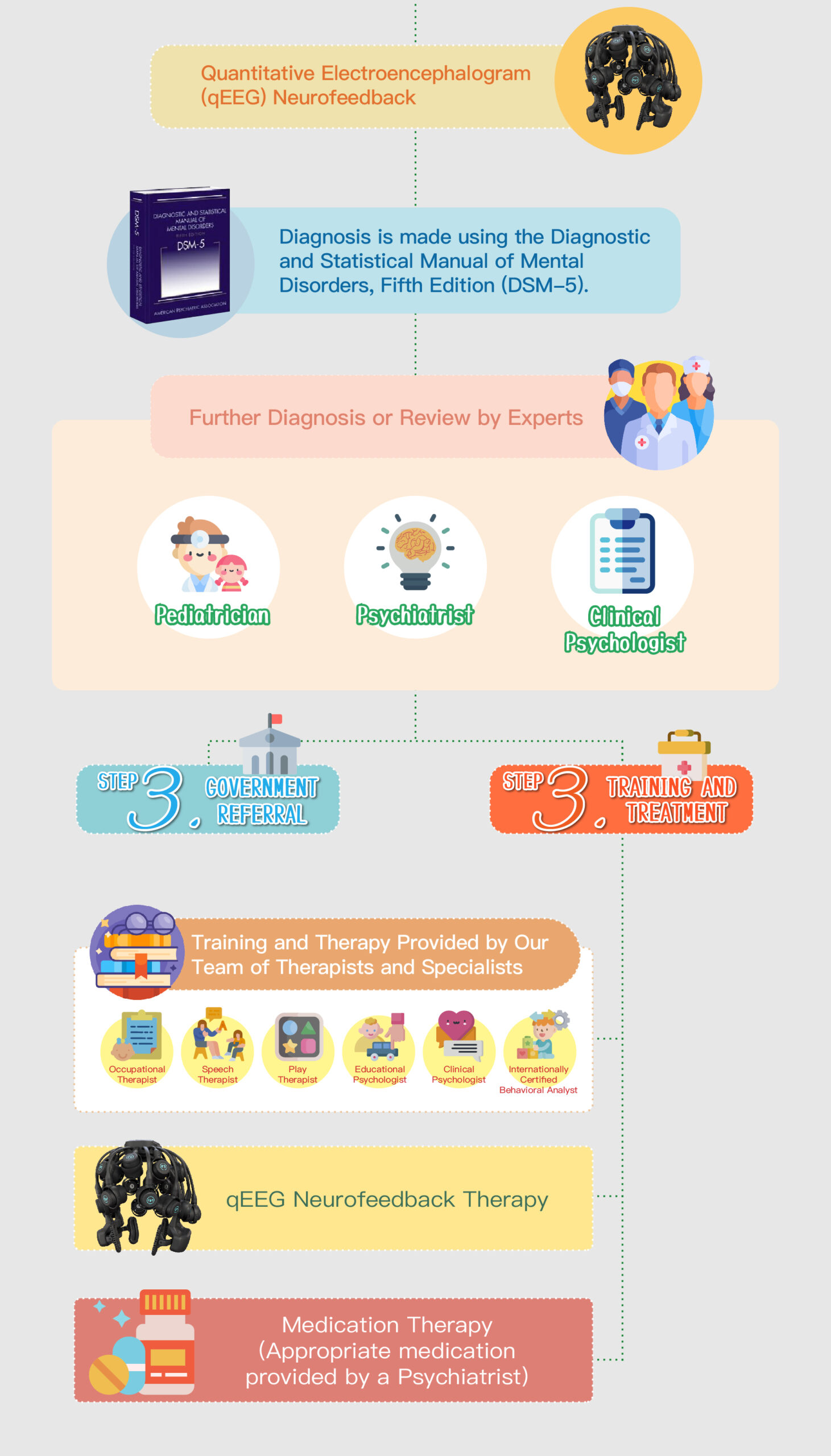
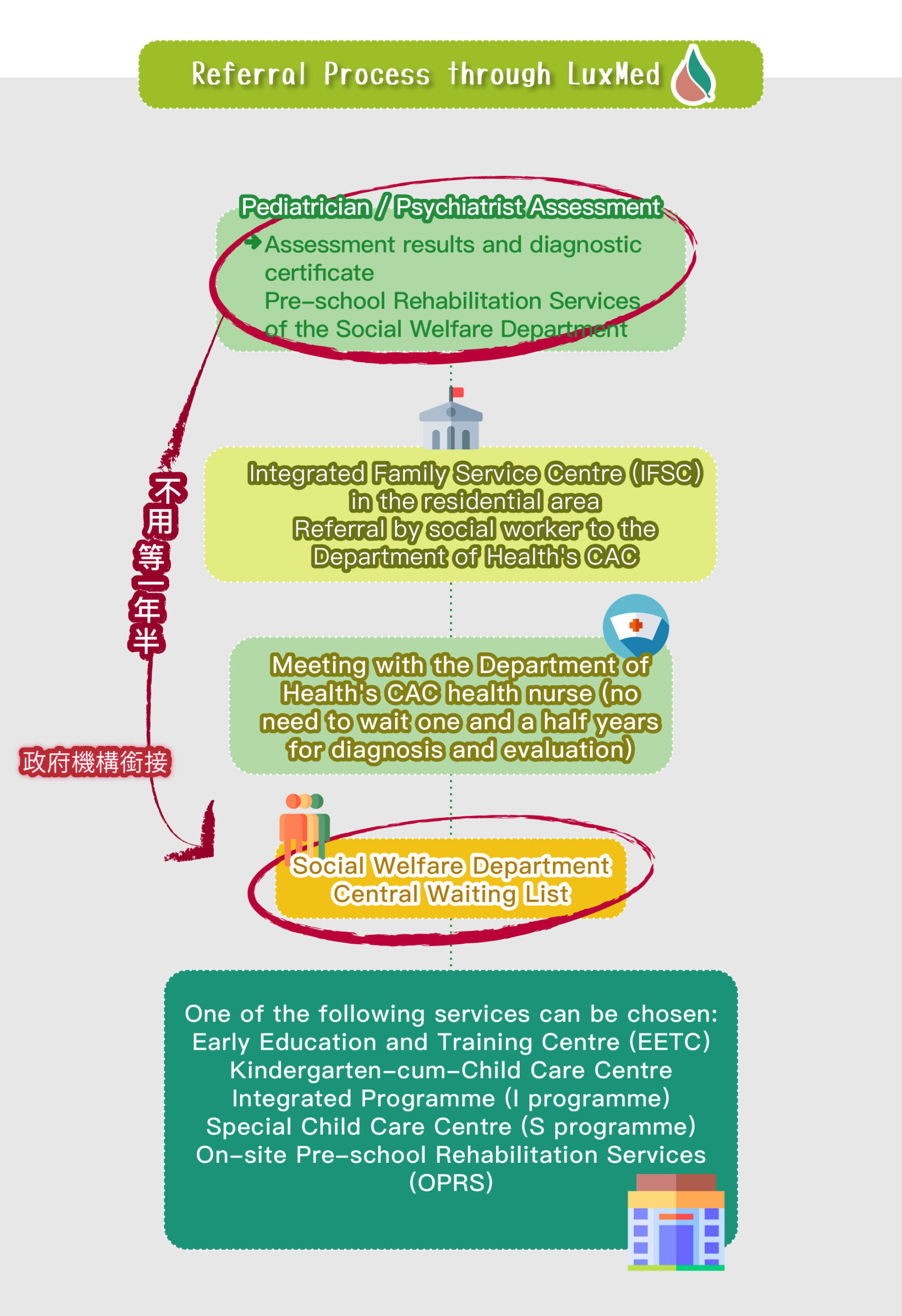
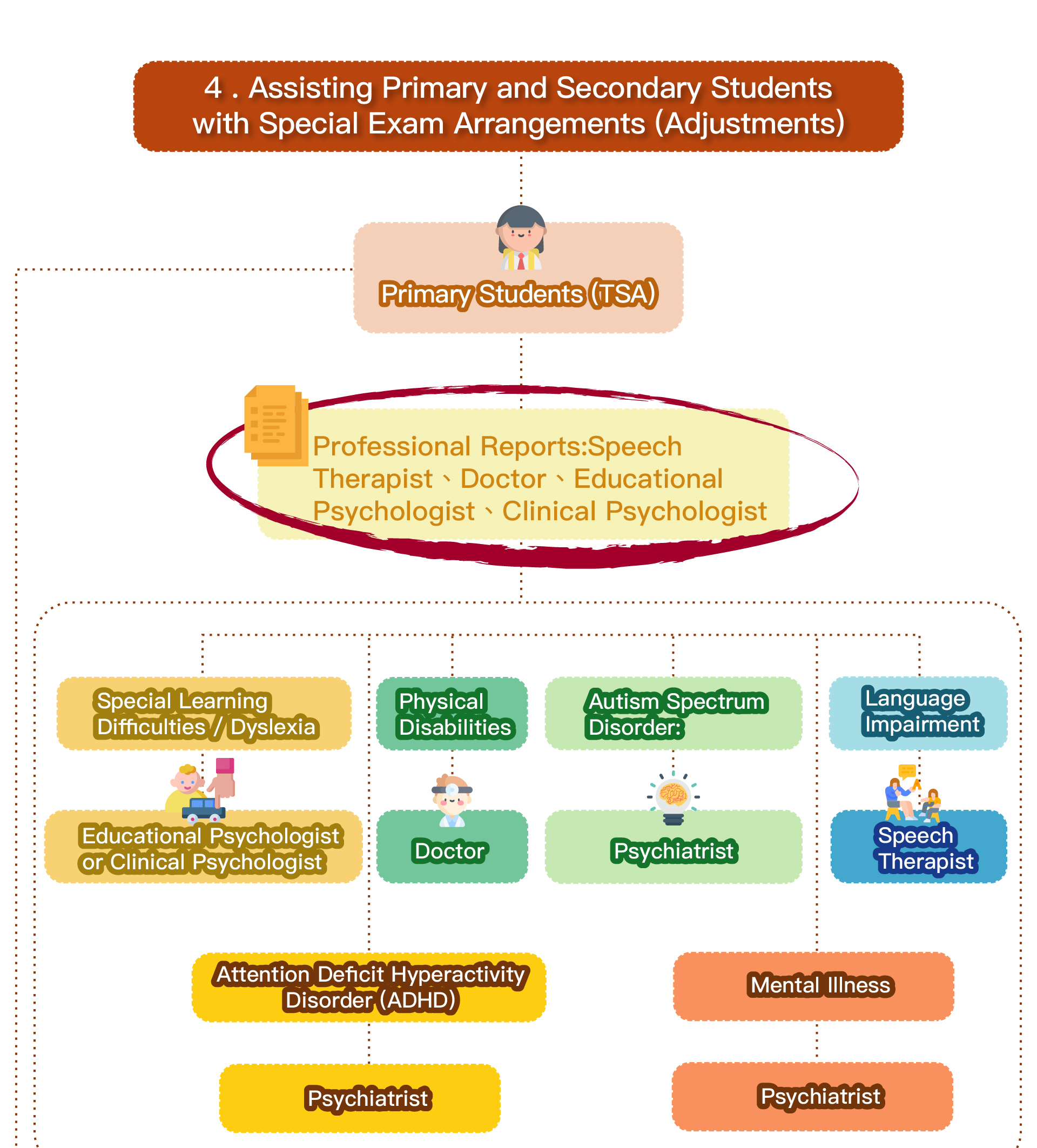
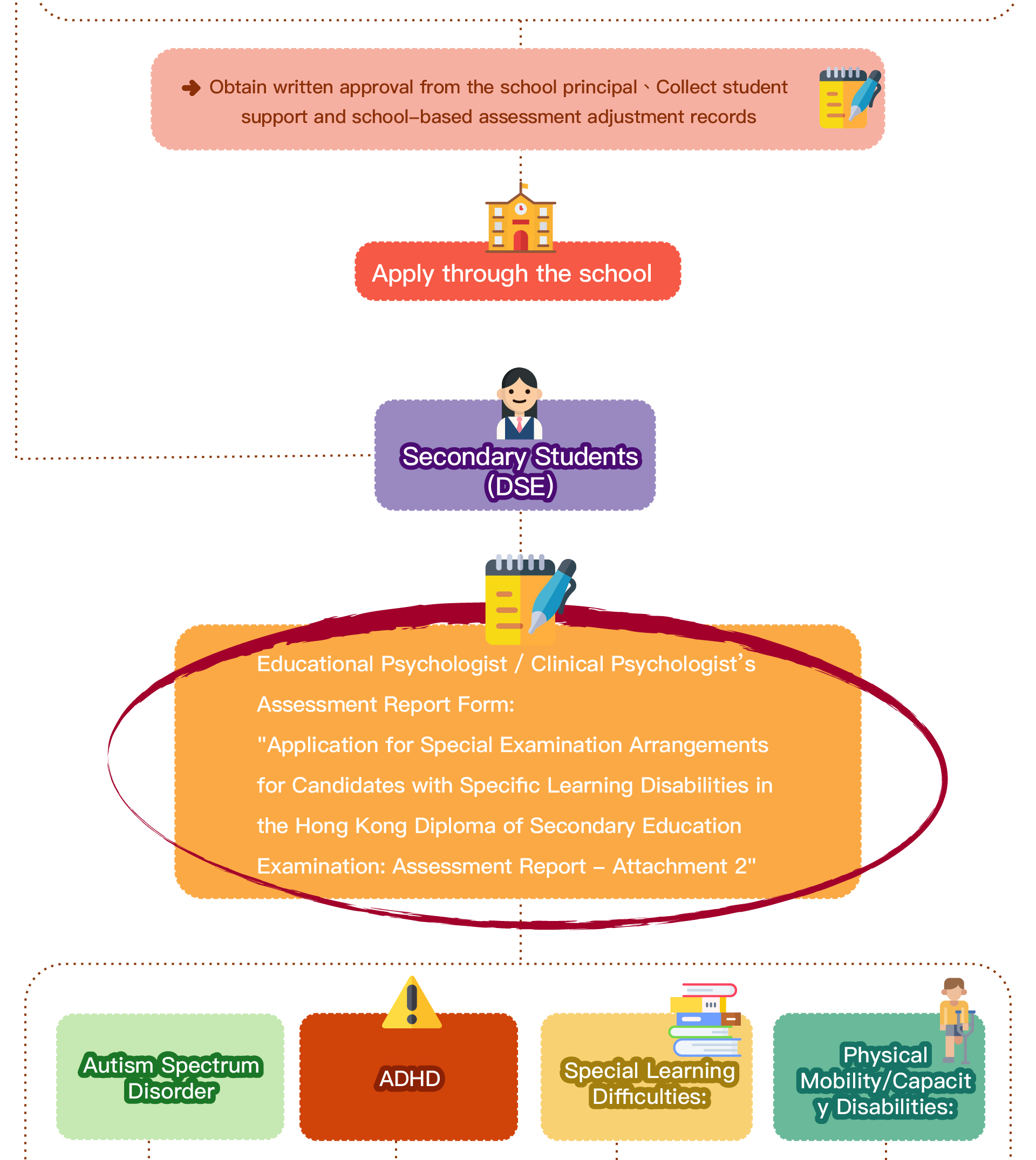
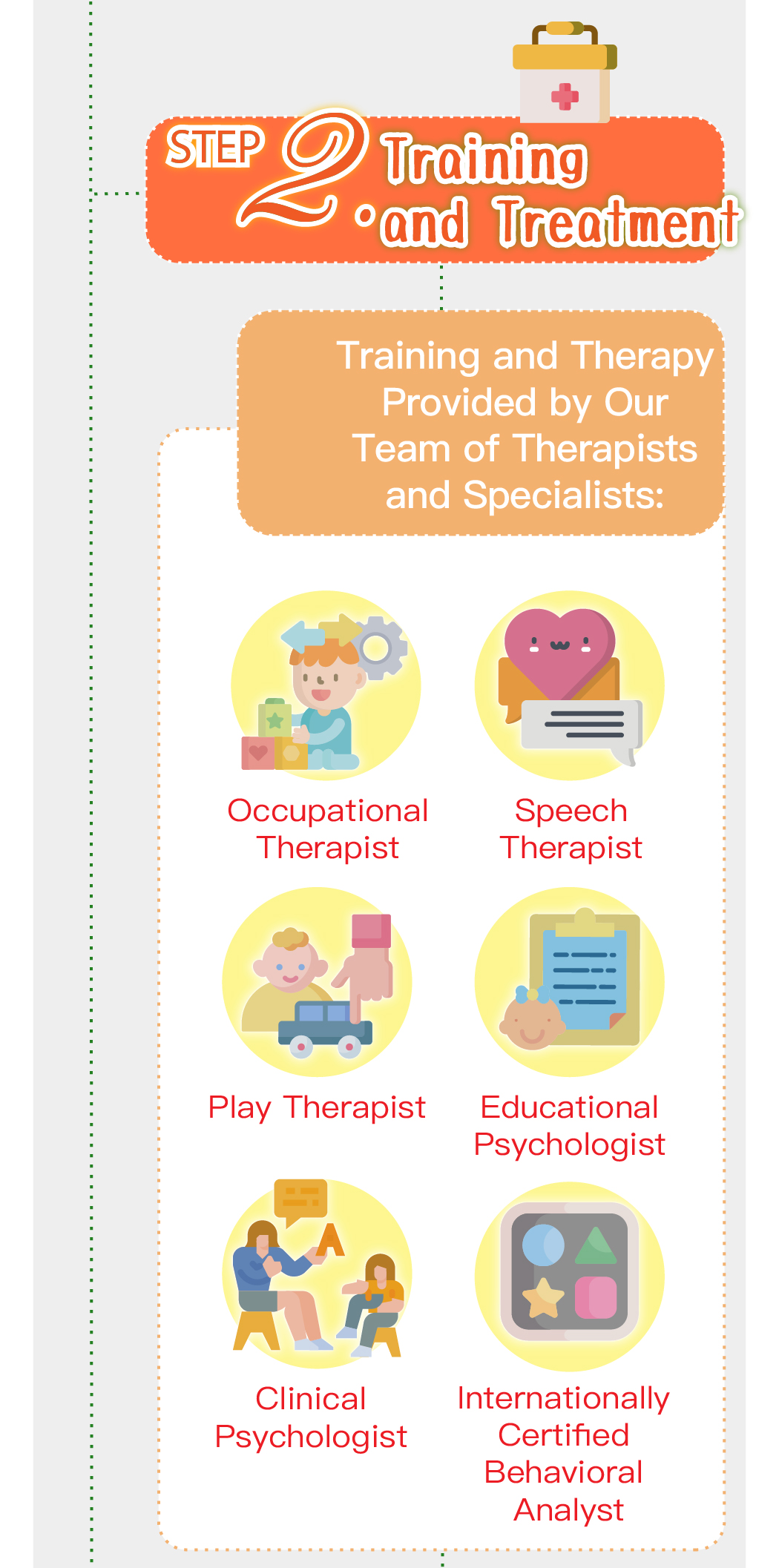
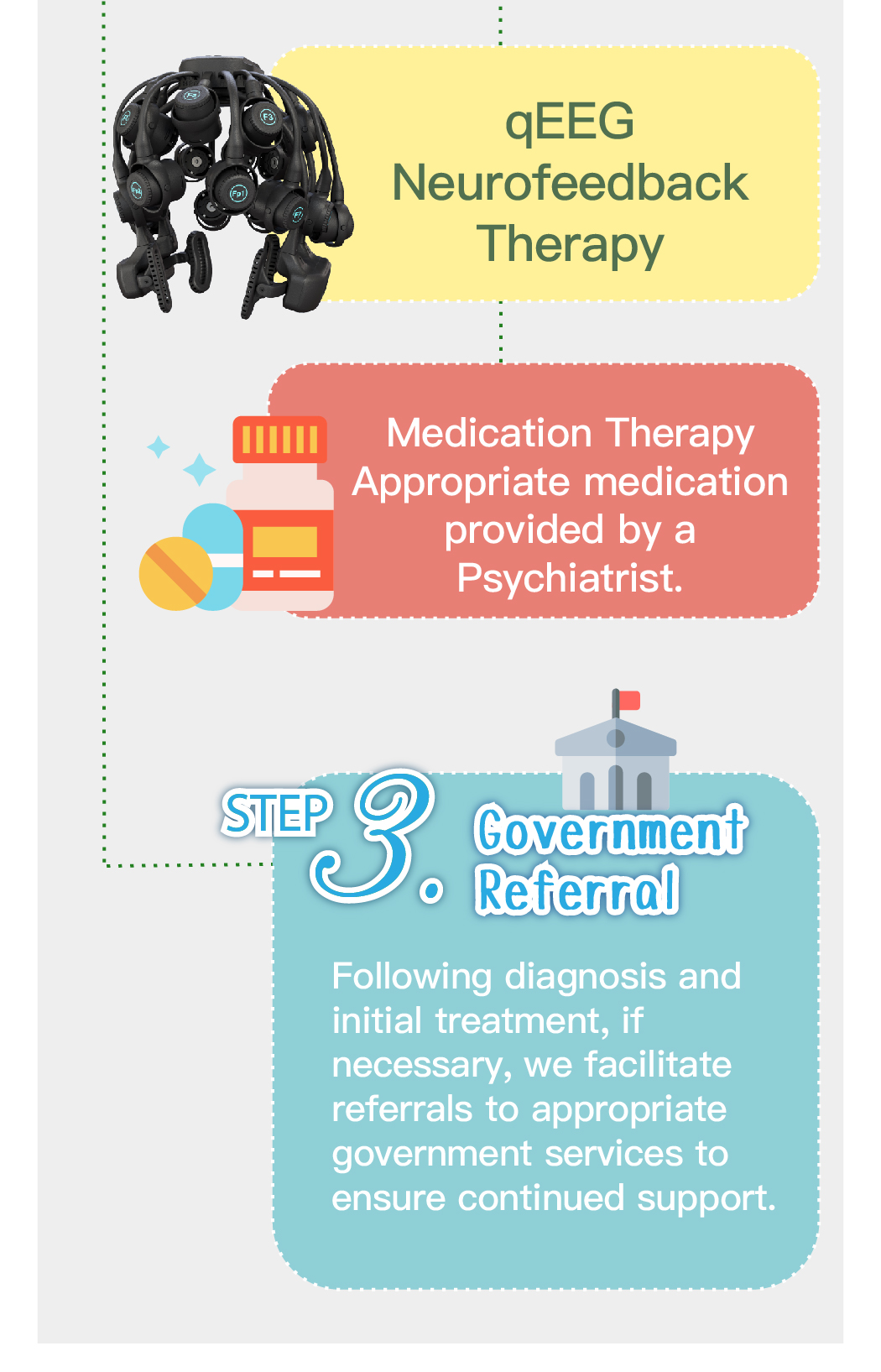
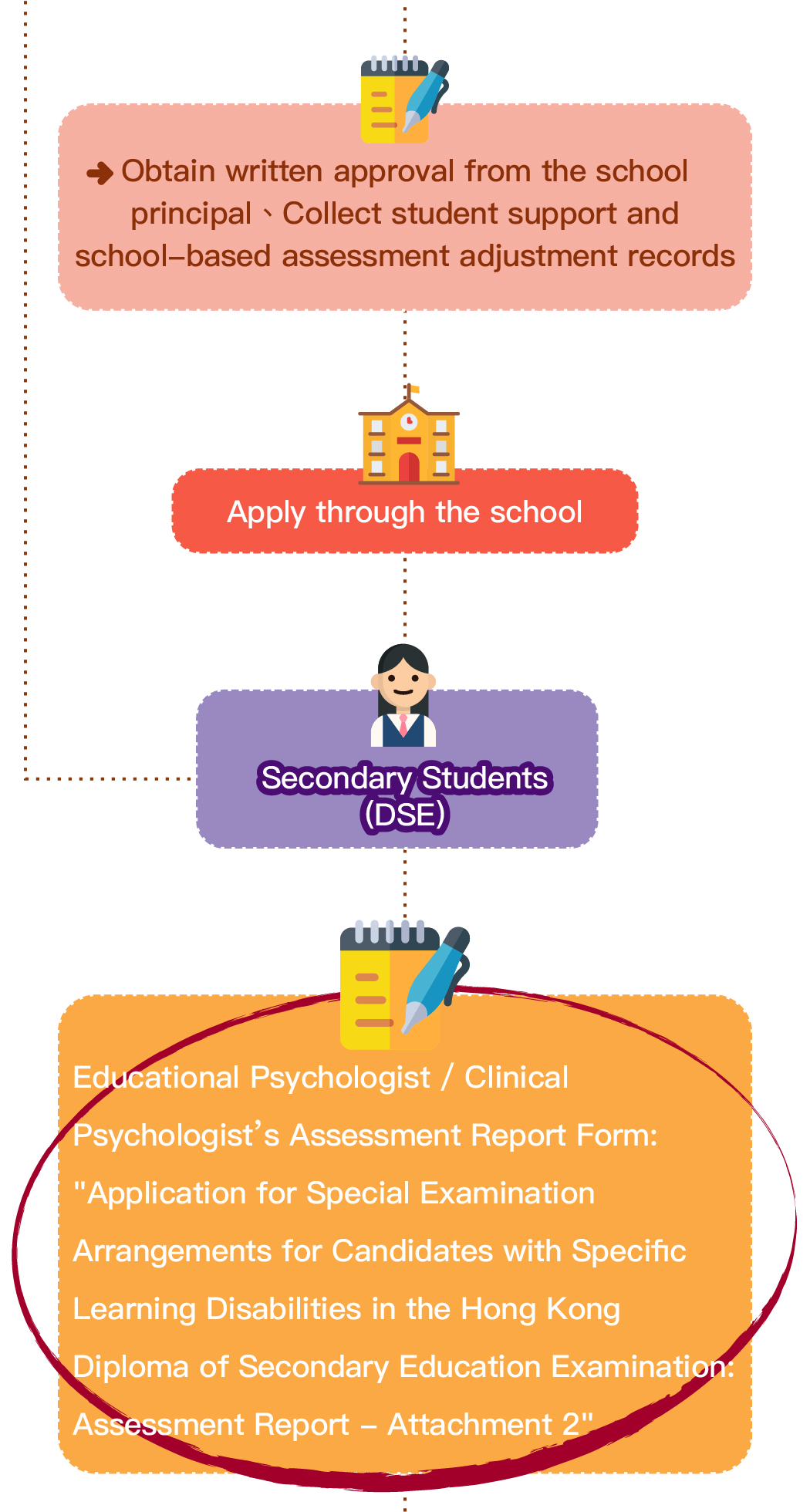
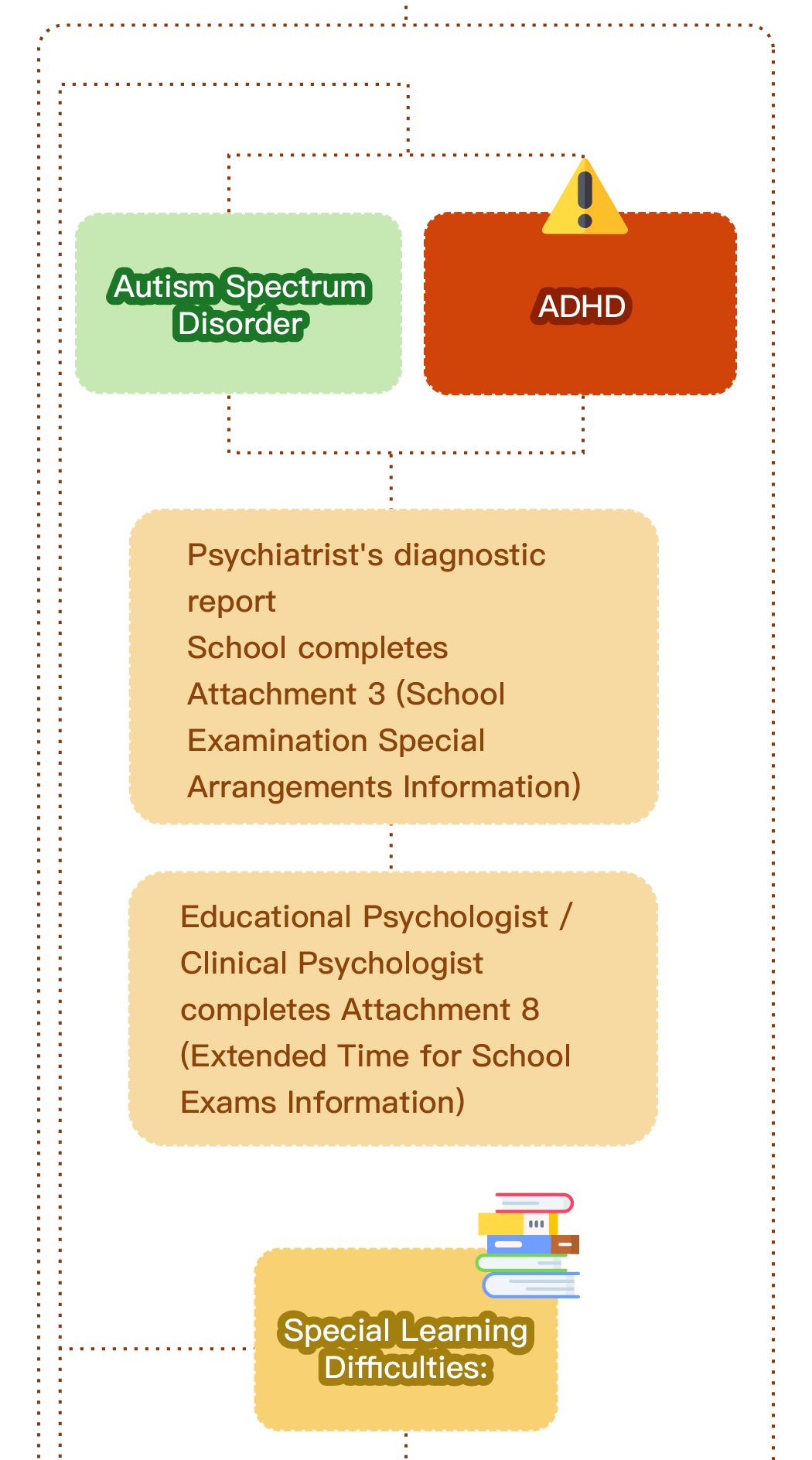
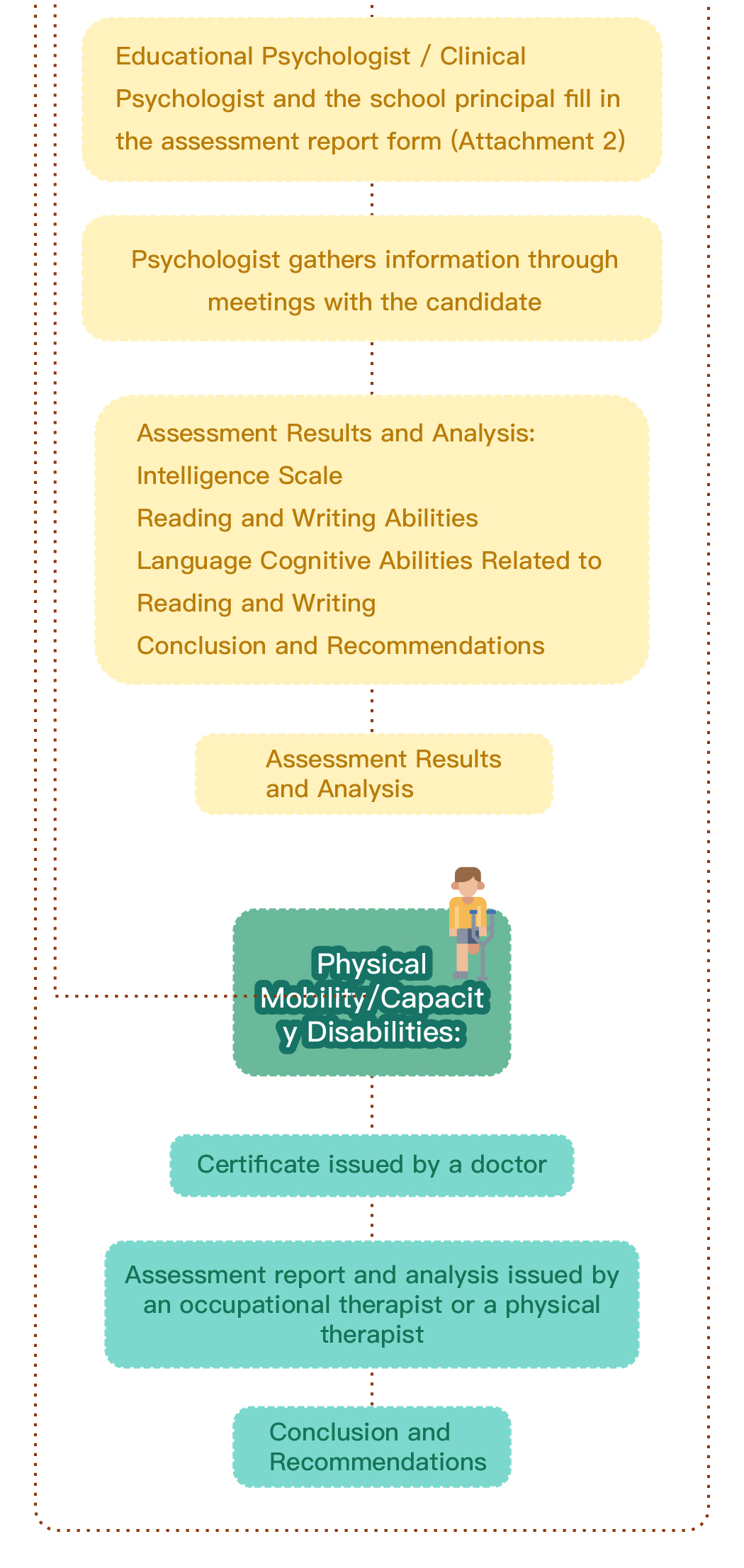
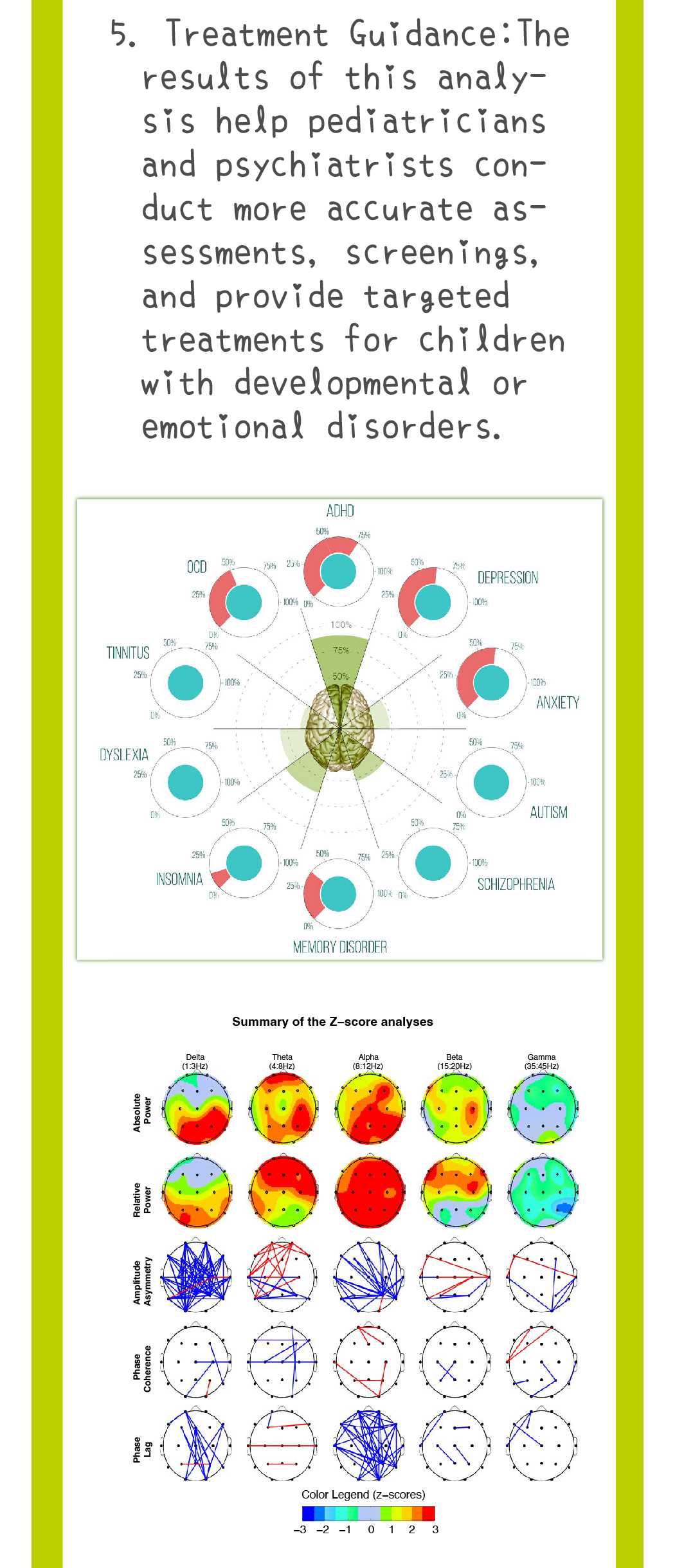
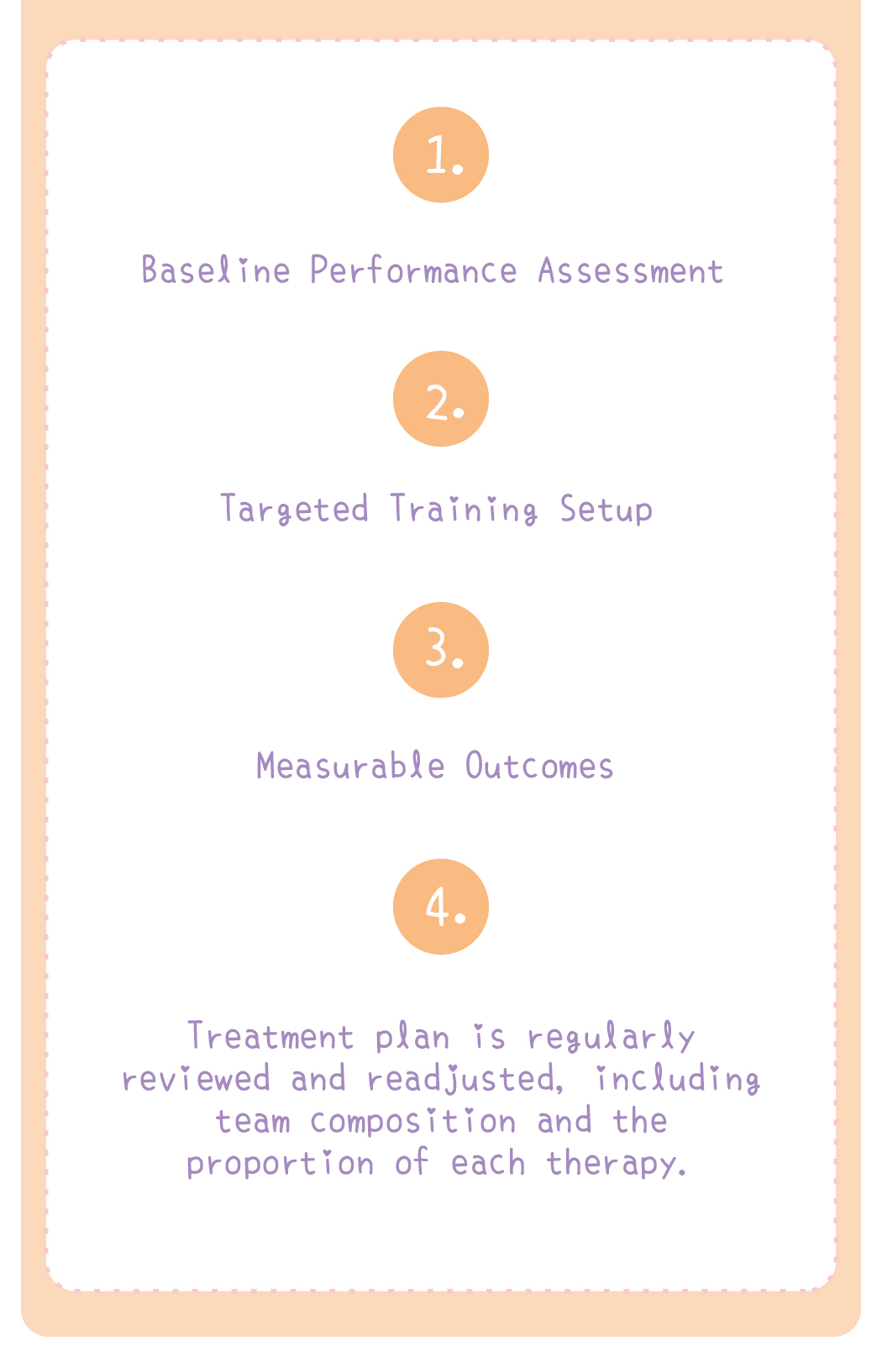
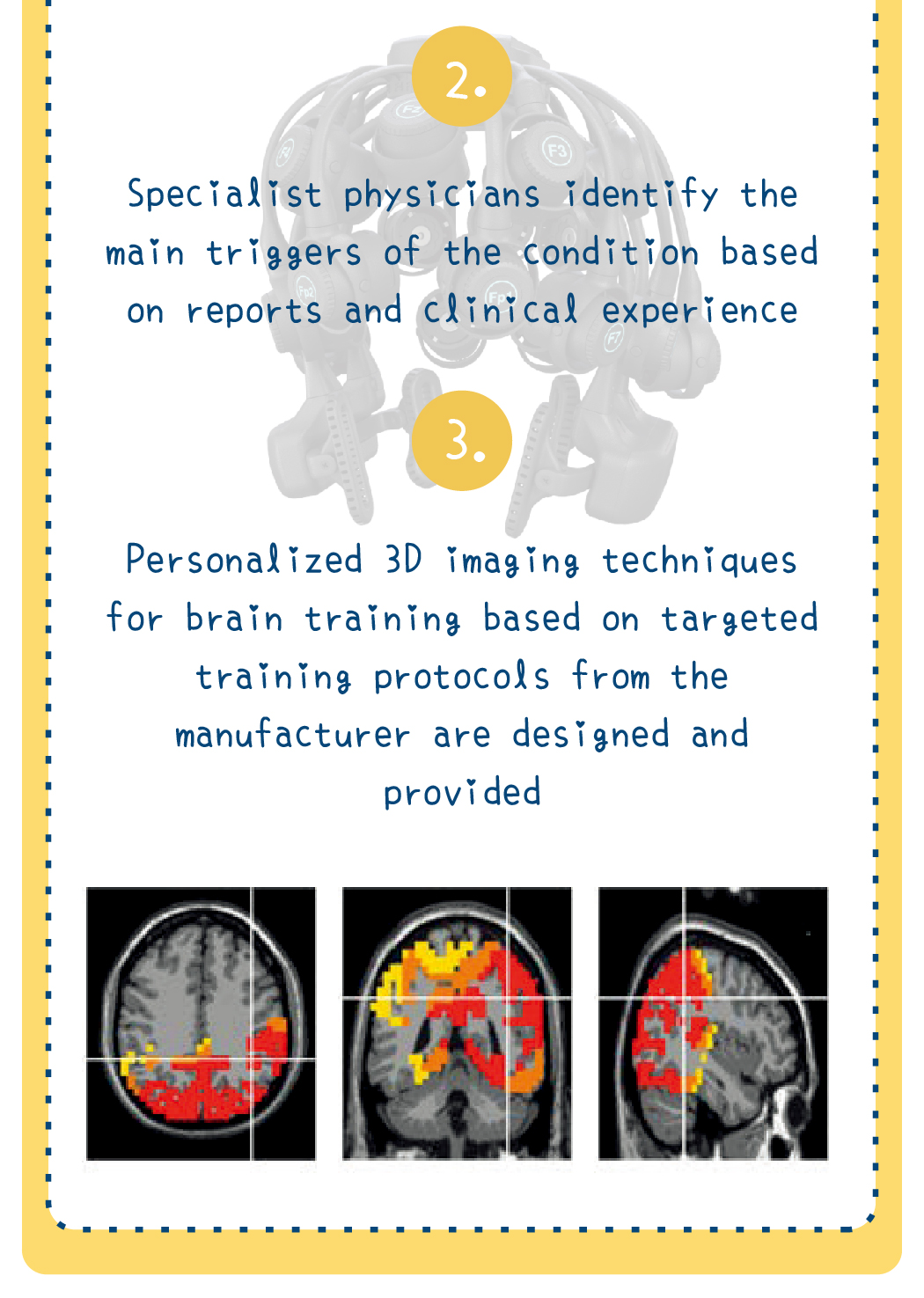
Speech therapy is a professional service designed for individuals who experience communication and swallowing difficulties. For children with autism, speech therapists assess their needs and create tailored treatment plans focused on areas such as comprehension, expressive abilities, social communication, oral motor skills, speech clarity, and swallowing function. Many autistic children exhibit language learning difficulties, such as delayed speech, providing irrelevant answers, brief responses, or using inappropriate words. Based on the child’s condition, speech therapists work to improve their pre-language skills, language comprehension, and expressive abilities. Therapists design activities to enhance the child’s motivation to communicate, attention span, ability to follow instructions, and problem-solving skills, while also training them to express themselves more clearly.
Even children with higher language abilities may experience difficulties in social communication, such as using stereotypical intonation or failing to understand others’ emotions. Speech therapists guide children to use appropriate tone, rhythm, and body language, helping them apply proper etiquette and behavior in various social contexts. Through Theory of Mind (ToM) training, therapists also help children better understand others’ thoughts and feelings, making it easier for them to build positive social relationships.
References:
Black, L. I., Vahratian, A., & Hoffman, H. J. (2015). Communication disorders and use of intervention services among children aged 3-17 years: United States, 2012 (pp. 1-8). Atlanta, GA, USA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics.
Paul, R. (2008). Interventions to improve communication in autism. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Clinics of North America, 17(4), 835–856.
















































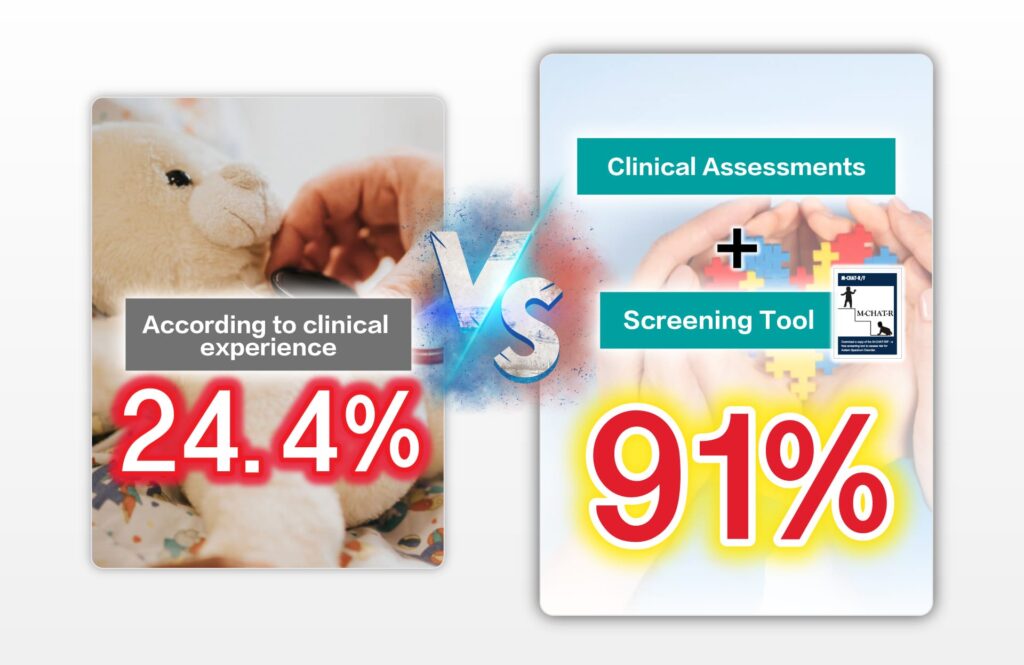
















_0-25.png)
_0-26.png)
_0-27.png)
_0-28.png)
_0-29.png)
_0-30.png)
_0-31.png)
_0-32-1.png)
_0-33-2.png)
_0-34-1.png)
_0-35-1.png)

























.png)


_0-50-1024x539.png)


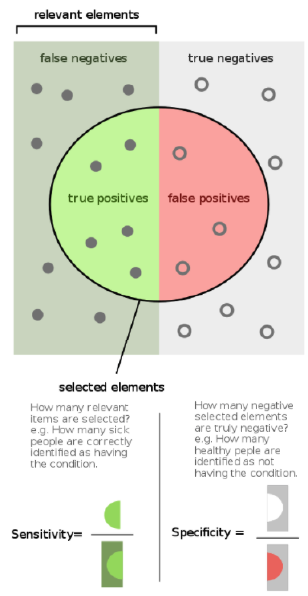












_0-54.png)
_0-55.png)
_0-56.png)
_0-57.png)
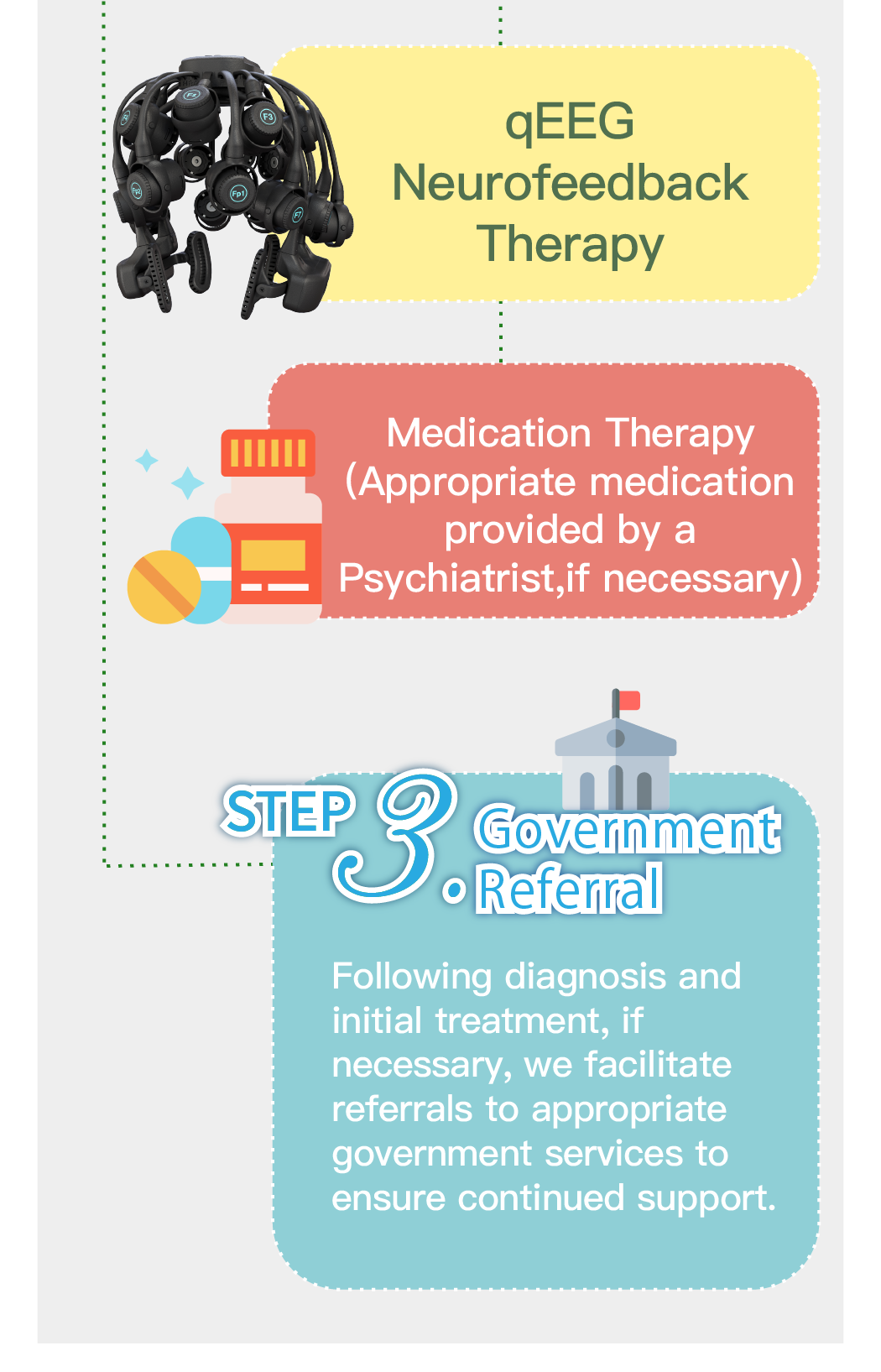
_0-59.png)


_0-62.png)
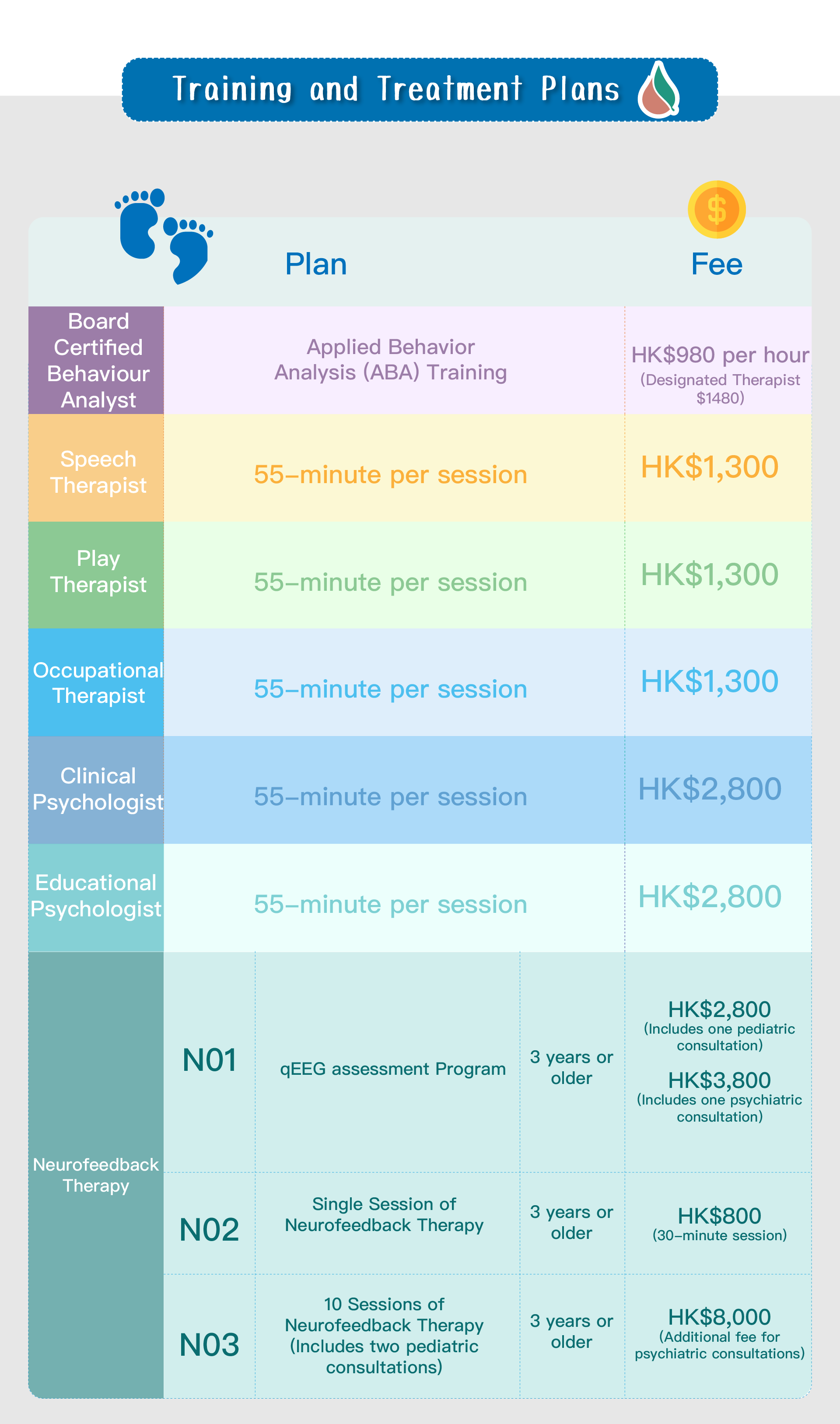
_0-64.png)
_0-65.png)
_0-66.png)
_0-66-副本.png)
_0-67.png)
_0-68.png)
_0-69.png)
_0-70.png)

_0-72.png)
_0-73.png)
_0-74.png)
_0-75.png)
_0-76.png)
_0-77.png)
_0-78.png)
_0-79.png)
_0-80.png)
_0-81.png)
_0-82.png)
_0-83.png)
_0-84.png)
_0-85.png)
_0-86.png)
_0-87.png)
_0-88.png)
_0-89.png)
_0-90.png)
_0-91.png)
_0-92.png)
_0-93.png)
_0-94.png)

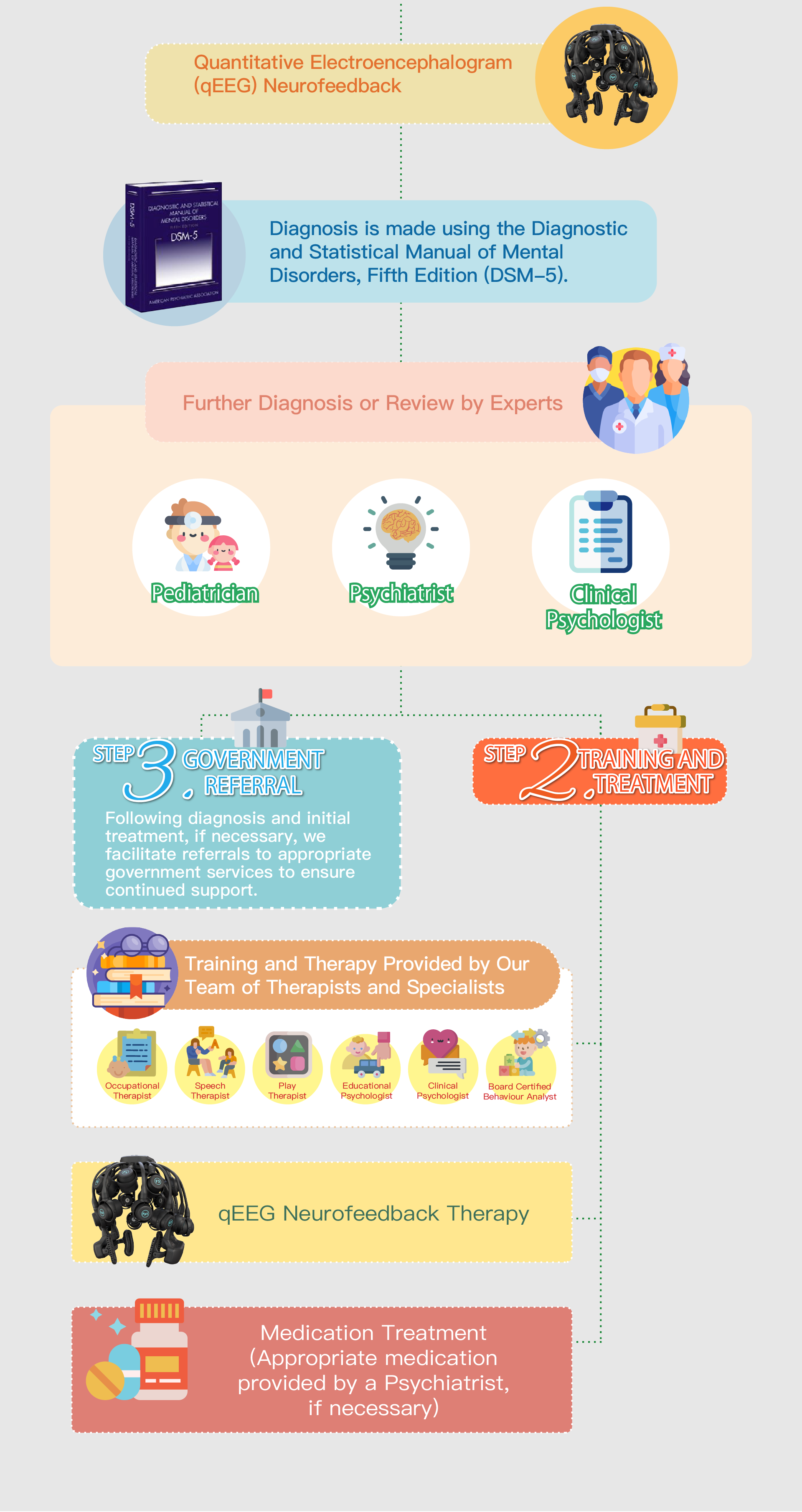





_0-62.png)